MATLAB Distributing Computing Server
Benefits of MDCS
MDCS enables users to submit both serial as well as parallel jobs to one of the central HPC clusters from within a local MATLAB session. There is no need to deal with SGE, or even to log-on to the HPC systems. The internal structure of the clusters is hidden, they merely act as a "black box" which is connected to your local machine and provides you with powerful computational resources. On the other hand, jobs submitted via MDCS are fully integrated into SGE, and have the same rights and privileges like any other SGE batch job. Thus there is no conflict between MATLAB jobs submitted via MDCS and standard SGE batch jobs.
Using MDCS for MATLAB computations on the central HPC facilities has a number of advantages:
- Simplified workflow for those who exclusively do their numerics with MATLAB - they can do development, production of results, and post-processing within a unified, user-friendly environment, without ever having to leave the MATLAB desktop
- A worker (= MATLAB session without a user interface) does not check out any of the "regular" MATLAB licenses (which, e.g., are needed by desktop users) and, what is even more, it also does not check out any Toolbox license even if functions or utilities of the toolbox are used; it merely suffices that the client from which the job was submitted can in principle check out the toolbox license (regardless if it is indeed checked out - that depends on what kind of computations run on the client).
Given that the University has only 200 MATLAB licenses, but there are 224 worker licenses available for the HPC systems it becomes clear that the total number of MATLAB licenses for all users in the University has effectively been more than doubled! - Calculations with more than 12 workers, significant peed-up by parfor loops and similar tools
Therefore, all MATLAB computations on the clusters should by default be done via MDCS. Of course, it is also possible to submit MATLAB Jobs as regular SGE jobs (by writing the command that starts MATLAB in non-interactive, non-GUI mode into the submission script and supplying the necessary input arguments and files), but this strategy is deprecated. It leads, due to the limited number of available MATLAB and, in particular, Toolbox licenses, to a strong competition between cluster users and other MATLAB users across the University. Moreover, cluster jobs often fail immediately after they have started to run since there are no free licenses available (a reliable, full license integrations with SGE is hard to implement, though possible in principle). With MDCS, these problems do not exist since SGE keeps track of the total number of workers currently used, and if the corresponding resources are not available, the job just stays in waiting state like any other batch job.
Prerequisites
- On your local machine (PC, workstation, notebook, ...), you must have one of the following MATLAB releases installed:
R2010b
R2011a
R2011b
Unfortunately, more recent releases of MDCS are currently not available. It is important that your local installation includes all toolboxes, in particular the Parallel Computing Toolbox (PCT). It is recommended to install MATLAB from the media provided by the IT Services on their website. In that case, all required components (including the PCT) are automatically installed. - You must install a couple of files into the directory
matlabroot/toolbox/local
(on a Unix/Linux system, analogously for Windows clients) - After these preparations, start a new MATLAB session and bring up the Parallel Configurations Manager by selecting Parallel -> Manage Configurations. Create a new "Generic Scheduler" Configuration (File -> New -> Generic):
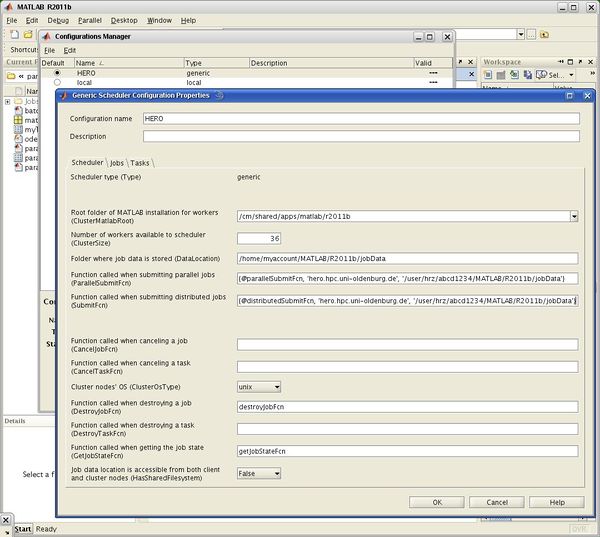
The following fields and boxes must be filled out:
- Name
After these preliminaries, you are prepared for exploring the rich possibilities of distributed and parallel computing with MATLAB!
Basic MDCS usage
Typical example of an "embarrassingly parallel" problem ("task-parallel" job in MATLAB terminology): parameter sweep of a 2nd-order ODE (damped Harmonic Oscillator).
ODE defined in odesystem.m.
Parameter sweep in param_Sweep_batch.m. Independent loop iterations automatically get distributed across 16 workers:
job = batch('paramSweep_batch', 'matlabpool', 15, 'FileDependencies', {'odesystem.m'});
Check state by 'Job Monitor or in command window:
job.State;
Analyze results:
load(job);
Runtime:
job.t1
Visualization:
figure;
f=surf(jobData.bVals, jobData.kVals, jobData.peakVals);
set(f,'LineStyle','none');
set(f,'FaceAlpha',0.5);
xlabel('Damping'); ylabel('Stiffness'); zlabel('Peak Displacement');
view(50, 30);
Clean up
delete(job);
All files can be downloaded from ...
Advanced usage: Specifying resources
Old (non-MDCS) MATLAB usage
To submit a MATLAB job, you must first load the environment module in your submission script:
module load matlab
This automatically loads the newest version, if several versions are installed. After that, invoke MATLAB in batch mode:
matlab -nosplash -nodesktop -r mymatlab_input
where mymatlab_input.m (a so-called ".m-file") is an ASCII text file containing the sequence of MATLAB commands that you would normally enter in an interactive session.
Slides and links from last MATLAB workshop at the University of Oldenburg (19.02.2013)
Slides
Links
- Parallel-Computing Toolbox
- Distributed Computing Server
- Distributed Computing Server Webinars
- Material for Academia